SMEs' journey to digital transformation

This blog is part of a CORE-Africa blog series on digitalization. The previous blogs in the series explored the constraints faced by SMEs in going digital and the benefits of going digital for SMEs. Here, we focus on undertaking a digital maturity and needs assessment of SMEs, as a first step in the SME’s journey to digital transformation.
Steps involved in SME digital transformation
Through digital transformation, SMEs can harness technology and use digital solutions to streamline their business activities and functions. It helps improve their productivity and profitability, while also enhancing their responsiveness to shocks and stresses as a consequence of climate change and other factors like COVID-19. Digital transformation is not just a process of using digital technologies within the company. It also requires some aligning of the company’s culture, structure, and processes to the digital strategies, so that the digital solutions can serve their ambitions best.
Digital transformation can therefore require significant change or evolution from the companies, along with considerable time, planning, and resources. The need for changes happening during the digital transformation journey may seem overwhelming for some companies, especially SMEs that have little experience in the digital domain. Further, mistakes made along the journey may be expensive and could harm their functioning. Therefore, digital transformation requires that the company management team fully understands the nature of change the transformation may bring and its impact on various parts and aspects of the company, so that they can make balanced decisions, choose realistic options, and take actions accordingly in a timely manner[1].
SMEs can use the following six step process[2] to begin their digital transformation journey.
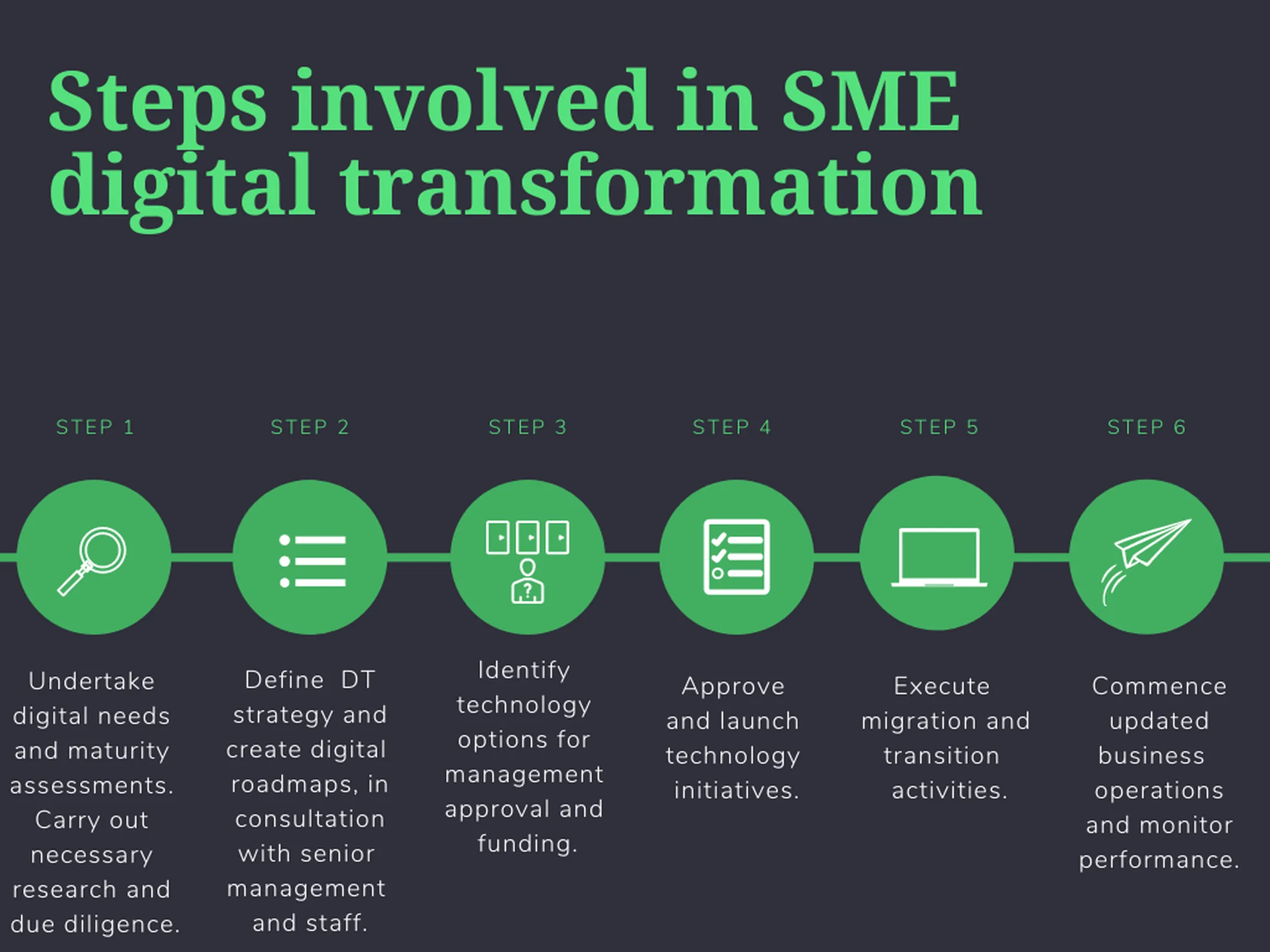
Steps involved in SME digital transformation
Ascertaining the digital maturity and digital needs of SMEs – The CORE Experience
As a first step towards digital transformation, SMEs will need to review their business processes, practices, workflows, and procedures, and understand their digital needs as well as digital maturity levels. Undertaking such needs and maturity assessments will allow the companies to prioritize their needs, and design customized digital strategies and roadmaps that they can invest in.
CORE-Africa created tools that can be used by micro, small and medium scale agribusinesses undertake digital maturity and needs assessments within the company. The digital maturity tool allows SMEs to rate their current levels of digital engagement and develop an idea of the possibilities for digital engagement in their company operations. The digital needs assessment tool dives deeper into the different departments and operations within the SMEs, enabling the SMEs to see what digital solutions they are already using, and what possibilities exist to improve efficiencies within their operations by adopting further digital solutions. You can reach out to our digitalization advisor for the tools.
The CORE project undertook digital maturity and needs assessments for 11 agribusiness SMEs supported by the Climate Resilient Agribusiness for Tomorrow (CRAFT) project – 5 in Tanzania and 6 in Kenya. Based on the digital development stage at which the SMEs were in, the project classified the SMEs into 4 phases of digital development[3] (as detailed below), recommended digital solutions to the SMEs that match their needs, and provided the SMEs with a tentative digital roadmap that they could use to drive investments into their digitalization efforts.
Foundational phase: SMEs that have just started their digitalization activities or are still in early phases of the process. Some individual employees have knowledge about challenges, benefits and business potential related to digitalization, but their understanding has not been collected systematically and the company does not have a formal digitalization plan. Digitalization is not yet on the company’s business agenda. These SMEs need external support in defining and implementing their digitalization journey.
Transitional phase: SMEs that already have some exposure to digitalization. These companies understand the potential of digitalization and have already started to define an overall digitalization strategy, or at least started testing and piloting digital solutions in selected business areas and functions. These companies still need external mentoring and support, but their internal staff with digitalization experience can champion the digital development of the company.
Accelerator phase: SMEs that already have a solid understanding of digitalization: its benefits, challenges, and requirements. They have defined their digitalization strategy and a continuous process of implementing it. These companies also have a systematic, knowledge-based approach for digitalizing and developing their products, services, and processes. They are ready to take charge of even major internal development projects, making the connections between various digitalization concepts and the goals of their organization.
Maturity phase: SMEs in this phase have a deep understanding of digital business models, product structures, processes, technologies, tools, and organizational models. Their organization and internal processes have been designed with digitalization in mind and are already reaping the benefits of digitalization.
The assessment highlighted the fact that the SMEs were at varying stages in their digital development and that none of the SMEs has yet reached a digital maturity stage. Two SMEs, one each in Tanzania and Kenya, were at an accelerated phase of digital development, where they have already adopted or tried different solutions, and understand which digital solutions to adopt and the overall direction they want to take. Three SMEs were at a transitional phase, where they have just started using digital solutions, and are looking for direction on which solutions to adopt/invest in going forward. However, most of the SMEs assessed were at a foundational phase, where they do not use any digital solutions and do not have much, if any, experience in digitalization. While these SMEs understand the possible benefits of digital solutions, there is a capacity and resource gap that needs to be addressed.
Based on the analysis of the SMEs’ maturity levels, the needs assessments, and the digital priorities of the SMEs, CORE provided customized feedback and recommendations to the companies. CORE also provided a tentative digital roadmap for the companies with timelines for undertaking the various steps towards digital transformation. Further, CORE also developed a tool that can enable the SMEs to shortlist digital solutions and solution providers that suit their needs best, allowing for a more targeted match-making process.
For SMEs at a foundational phase of digital development, CORE recommended that they use a digital ladder of sorts - tackling their most urgent digital needs first. For instance, for one of the SMEs at a foundational level in Tanzania, their most urgent need was to improve their financial records management. They had tried to use a digital financial solution in the past, but it was not suited to their needs. They also had a capacity issue in using the solution. CORE's recommendation was to match the company with consulting service providers who can implement a range of financial management solutions and provide the necessary training and after-sales support that would be required.
For SMEs in the transitional phase of digital development, CORE linked the companies to enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution providers, that have different modules that cover all their operations. These ERP solutions enables businesses to consolidate information from their different operations and streamline processes.
For SMEs in the accelerated phases of digital development, CORE provided linkages to business analytics software and firms that can enable them to create dashboards that integrate information from the many softwares they already use in the company. This allows the companies to improve overall company efficiencies, and improve their business forecasting, allowing for more strategic decision making in the firm.
CORE is currently engaging with different digital solution providers identified in Kenya and Tanzania.
As a next step, CORE in collaboration with the CRAFT team, will work with the SMEs to match with the recommended digital solution providers, that can help the SMEs begin their digital transformation journey.
Written by: Vandana Thottoli, Business & Partnership Advisor.
Next blog: the next blog will follow an SME’s journey in using a digital solution and their experiences along the journey.
References
[2] Build a digital transformation roadmap in 6 steps
[3] Adopted from the results of “Smart Latvia” project by Diginn.